Pupillary assessment can be classified as one of the most critical aspects in the field of neurological assessment. This basic yet very effective analysis offers important information about the activity of the autonomic nervous system and can suggest different neurological disorders. Modern technology has seen improvement in the method used in the pupillary reaction assessment. This article focuses on the current advancements in pupil measurement to demonstrate that these neurological tools are useful in practice.
EVALUATION OF PUPILLARY REACTIVITY
The pupillary exam is a part of the neuro exam through which the physician examines the size, shape, and light response of the pupils. This assessment is important because it may unveil information concerning the condition of the cranial nerves most importantly the optic (CN II) and the oculomotor (CN III) nerves. The altered pupillary reaction is, therefore, a pointer to raised intracranial pressure, herniation, or optic neuropathy. In the past, clinicians carried out this assessment with the help of a flashlight and naked-eye vision. Earlier, this was a lengthy process but the new sophisticated neurological tools have made this a more accurate procedure and also diagnostic in many cases.
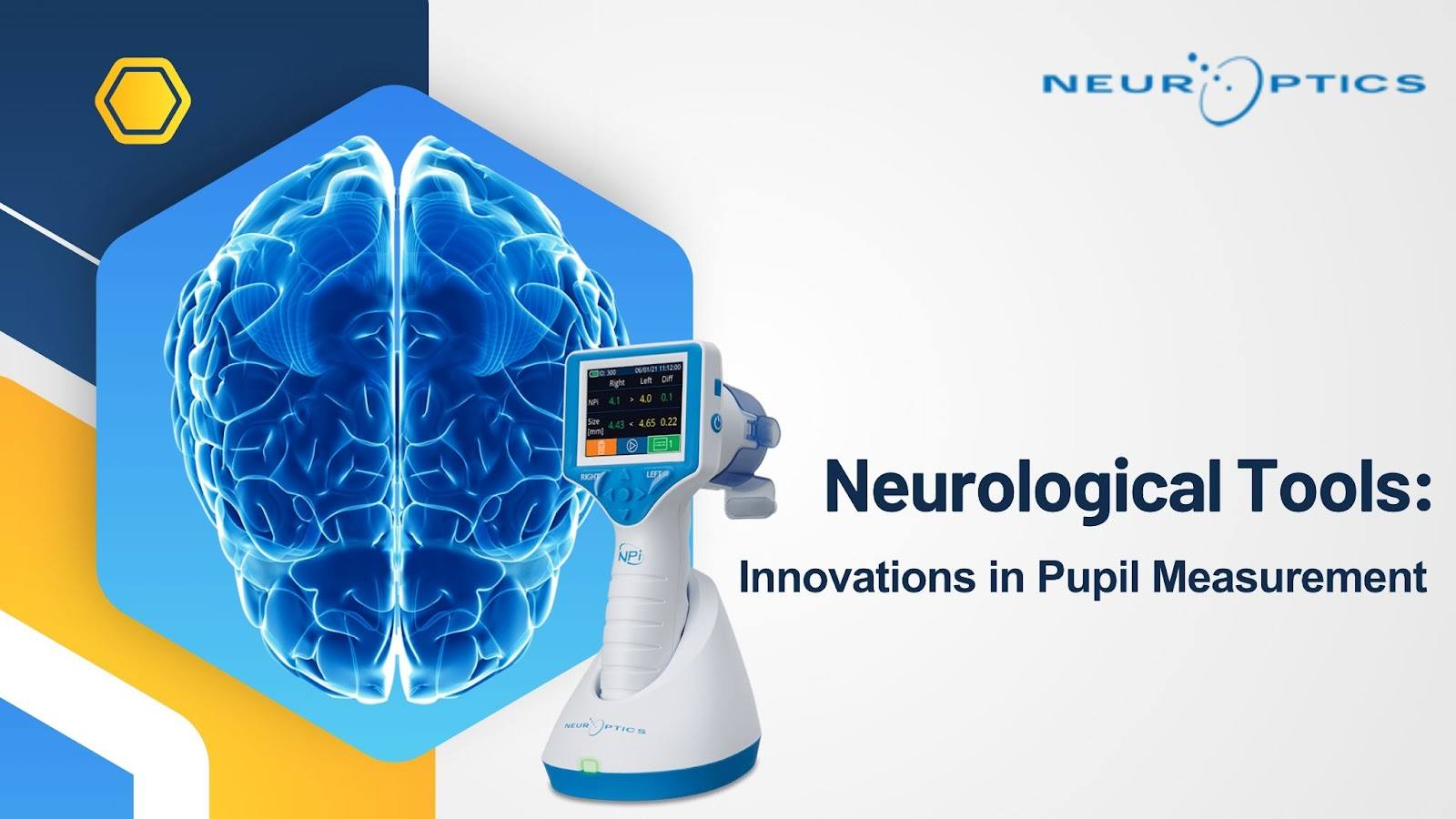
What’s Pupilometer?
The pupillometer is one of the most innovative inventions in the neuro exam area. This is a small, easily transportable tool used to assess the accuracy of the PLR. Unlike conventional approaches where pupil size is estimated through observation, the pupilometer measures the size of the pupils, the reaction time, and the constriction velocity, and thus is vital in diagnosing neurological illnesses.
The utilization of a pupillometer eliminates the chances of bias and poor correlation between different observers. This is particularly beneficial in critical care settings, where accurate assessment of neurological status can be life-saving. Also, owing to the PPG’s sensitivity to even the slightest variations in the pupillary reaction, it proves inestimable for the recognition of the first signs of neurological decline.
The Neurological Pupil Index (NPi)
Another major step in assessing the pupil’s characteristics is the creation of the Neurological Pupil Index (NPi). The NPi is an index computed from different aspects of pupillary response such as the diameter, reaction delay, and rate of constriction and dilation. This standardized score of pupillary evaluation varies between 0 and 5, and below the score of 3, the pupillary function is considered to be pathological.
The NPi provides a quantifiable measure of neurological function, enabling clinicians to track changes over time and make informed decisions regarding patient care. It is most effective in patients who have sustained a head injury, stroke, or any other ailment of the central nervous system. The continuous monitoring of the NPi enables the detection of early signs of neurological deterioration and thus addresses the issue on time.
Applications in Clinical Practice
The use of the pupilometer and NPi in evaluation of pupillary reaction has significantly transformed neurological assessments. In intensive care units, these tools are used when caring for patients with severe head injuries so that any shift in neurological state can be noticed, and necessary action taken. In emergency departments, quick and correct assessment of the pupil’s condition can provide information toward the identification of an acute neurological event and appropriate management.
In addition, these tools are crucial in research facilities as accurate measurement of the pupillary reaction is critical in understanding the impact of the majority of neurological disorders and treatments. Thus, the objective measurements given by the pupilometers and the NPi can help increase the validity of the study results, which can further develop the neurological science field.
Conclusion
As for neurological tools, advances especially in the assessment of the pupils have helped the neuro exams to become more precise and less prone to errors. The pupillometer and the Neurological Pupil Index are big innovations that give clinicians measures that are much more objective and enable them to diagnose and monitor neurological disorders in a much better way. It can safely be said that along with advancements in technology, these tools will be even more integrated in the assessment of neurological disorders, thereby improving patient care and outcomes.